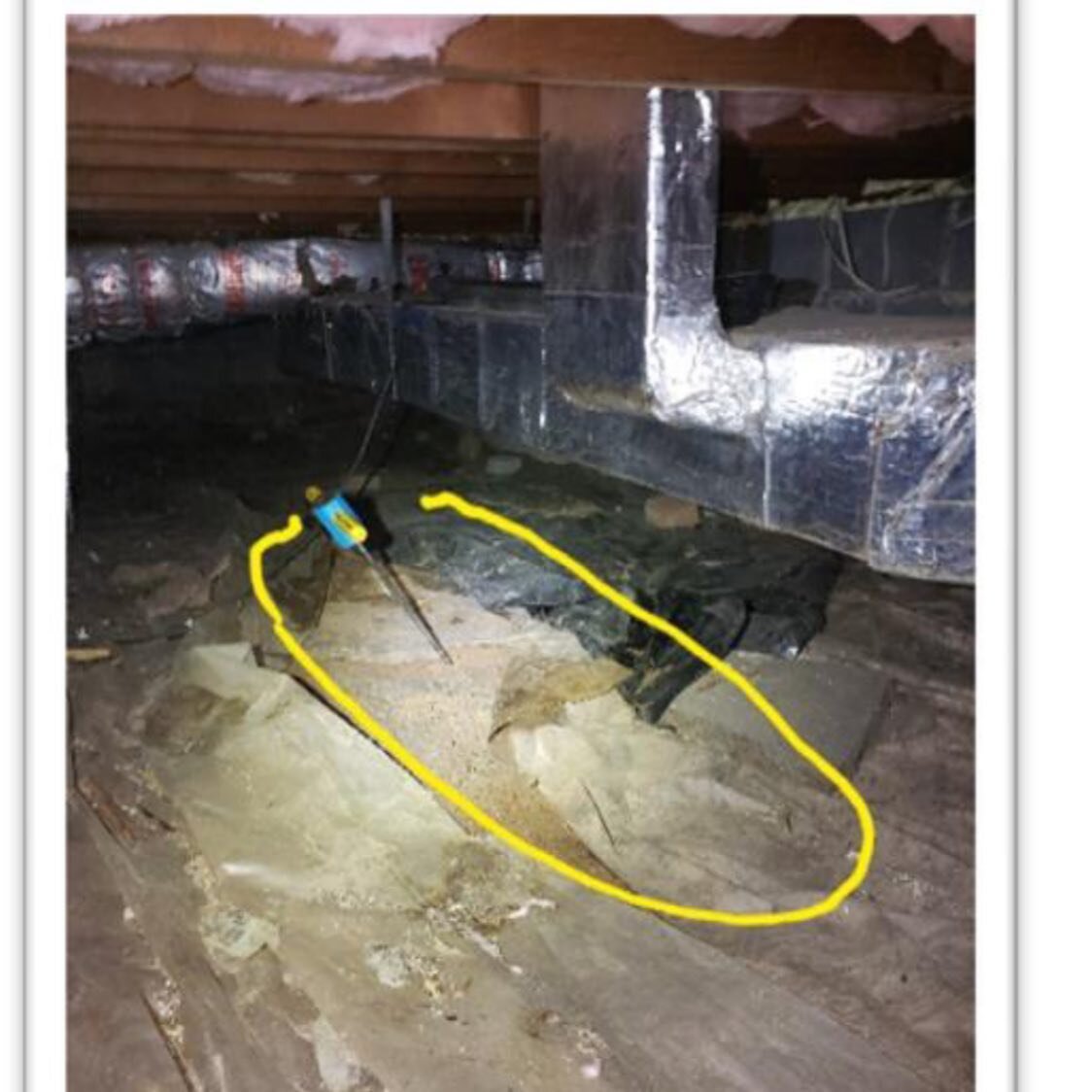
How Does GPR Concrete Scanning Work?
GPR concrete scanning may sound complicated, but it's a fascinating process that tells us what lies beneath the concrete surface without drilling or digging up. This blog will unfold the mystery of GPR concrete scanning in simple, engaging terms.
What is GPR Concrete Scanning?
GPR concrete scanning is a sophisticated technology used in the construction, engineering, and maintenance industries to examine the hidden world inside concrete structures. This technique utilizes ground penetrating radar (GPR) to identify, locate, and map out the position of various objects such as rebars, conduits, post-tension cables, and even voids within the concrete.
The principle behind GPR involves emitting radio waves into the concrete and capturing the echo that bounces back from any embedded objects. The strength and time it takes for the echo to return help in determining the depth and size of the object. This non-destructive method allows for detailed analysis without causing any harm to the existing structure.
The Science Behind GPR Scanning
At its core, GPR technology harnesses the power of electromagnetic radiation in the microwave band of the radio spectrum. When these radio waves encounter different materials or objects, they reflect back at various speeds and strengths, creating a profile or image of what lies beneath the surface.
The science is underpinned by Maxwell’s equations, which describe how electromagnetic waves propagate through different media. The ability of GPR to differentiate between types of materials relies on the fact that every material has a unique dielectric constant, influencing how it reflects or absorbs these waves.
How GPR Differs From Other Scanning Methods
Unlike X-ray imaging, which requires direct access to both sides of a concrete structure and exposes operators to harmful radiation, GPR scanning is a safer and more flexible alternative that only needs access to one side of the slab. Moreover, GPR can be conducted in live environments without evacuating the surrounding area, making it a preferred choice for busy construction sites.
Additionally, while methods like ultrasonic testing and radiography offer insights into the internal composition of concrete structures, GPR stands out due to its ability to conduct quick scans over large areas, providing real-time data that can be immediately analyzed.
The Step-by-Step Process of GPR Scanning
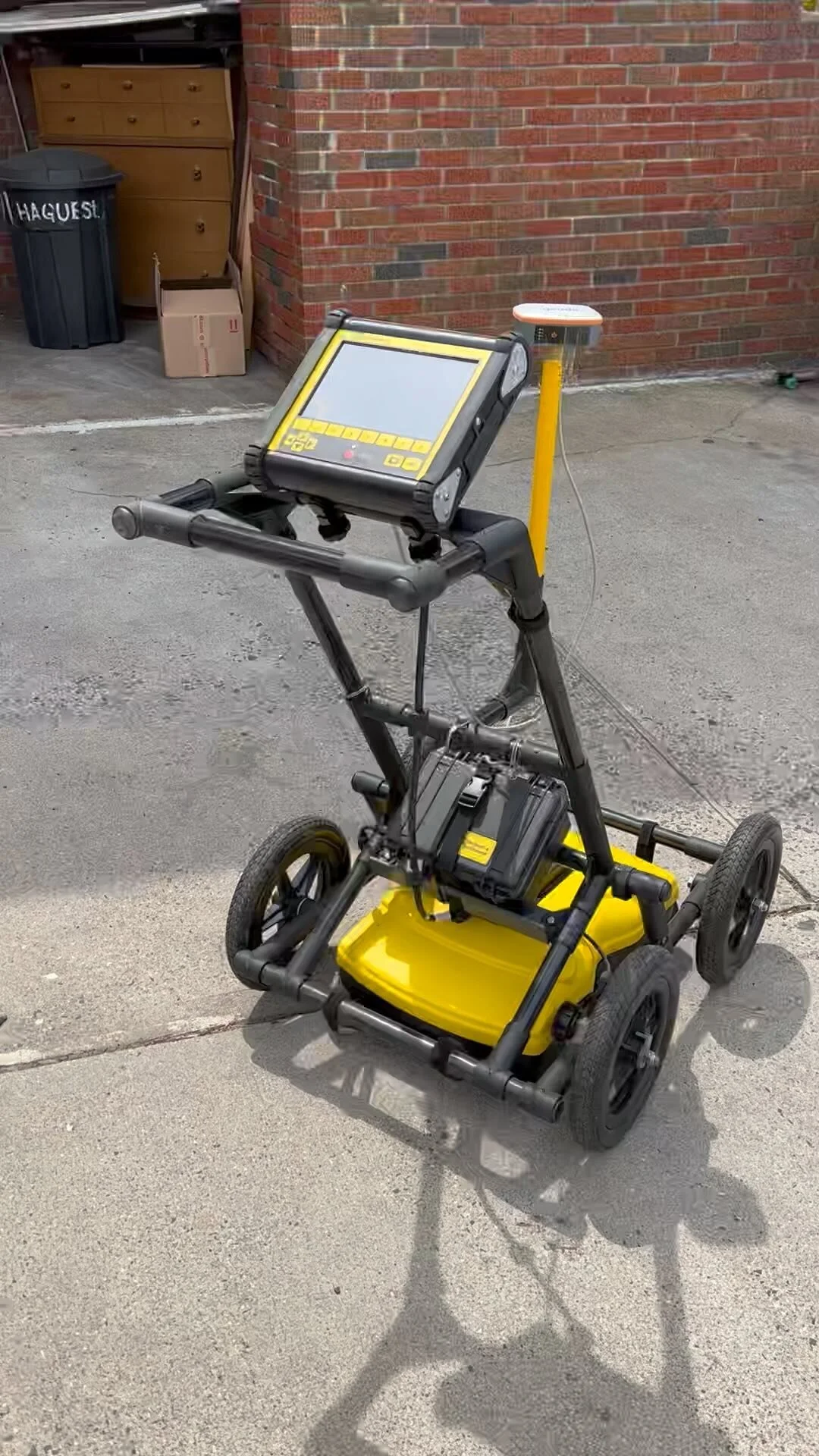
The process of GPR scanning begins with setting up the GPR equipment, which typically involves a mobile unit equipped with a transmitting and receiving antenna. As the equipment is manually pushed over the concrete surface, it emits electromagnetic waves into the slab.
These waves penetrate the concrete until they hit an object or material boundary, at which point the waves are reflected back to the surface and captured by the receiving antenna. Sophisticated software then interprets these signals to map out the subsurface features, identifying potential hazards or areas of interest.
Applications of GPR in Concrete Scanning
GPR concrete scanning has a wide array of applications including, but not limited to, locating rebar and tension cables prior to drilling or cutting, identifying and mapping the position of electrical conduits to avoid accidental breaches, and detecting voids within the concrete that could affect structural integrity.
Its versatility also extends to evaluating bridge decks for deterioration, inspecting buildings for structural defects, and assisting in the safe planning of renovations or extensions to existing structures.
Benefits of Using GPR for Concrete Assessment
One of the key benefits of using GPR for concrete evaluation is its non-destructive nature, enabling thorough assessment without compromising the structure. Additionally, this method substantially reduces the risk of injury to workers by locating hidden dangers such as live electrical conduits.
Moreover, GPR scanning saves time and money by preventing potential structural damage that could result from drilling into critical reinforcements, thereby avoiding costly repairs and project delays.
Understanding the Limitations of GPR Concrete Scanning
While GPR concrete scanning is immensely beneficial, it's important to recognize its limitations. The effectiveness of GPR can be influenced by the material's properties; for instance, very dense or highly conductive materials can diminish the depth of wave penetration, limiting the detection of objects within thick slabs.
Additionally, the accuracy of GPR data can vary based on the skill and experience of the operator, underscoring the need for expert analysis to correctly interpret the results.
Choosing the Right GPR Concrete Scanning Expert
Selecting a qualified GPR concrete scanning expert involves looking for a provider with extensive experience, not just in GPR technology, but also in understanding the complex interactions between electromagnetic waves and various construction materials.
The right expert will have a track record of successful projects and should be able to provide detailed case studies or references. Furthermore, they should offer a comprehensive service that includes not only the scanning process but also data analysis and clear reporting to guide subsequent construction work.
Wrapping Up the World Beneath
Understanding GPR concrete scanning can change the way we approach construction and renovation projects. By leveraging this non-intrusive method, we can ensure the safety, integrity, and efficiency of our work. Remember, the next time you see a construction team scanning the ground, they're probably using GPR to peek into the hidden world beneath the concrete.